No, coffee won’t keep you up at night – but smoking and alcohol might
06/10/2020 / By Divina Ramirez

Between 50 to 70 million adults in the U.S. alone suffer from a sleep disorder, according to recent reports from the American Sleep Association (ASA). In some cases, sleepless nights are linked to chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease and certain cancers.
Drinking coffee in the evening is also often reported to have a negative impact on sleep due to caffeine’s natural stimulating effects. But recent research published in the journal Sleep revealed that drinking coffee within four hours of bedtime does not affect sleep at all.
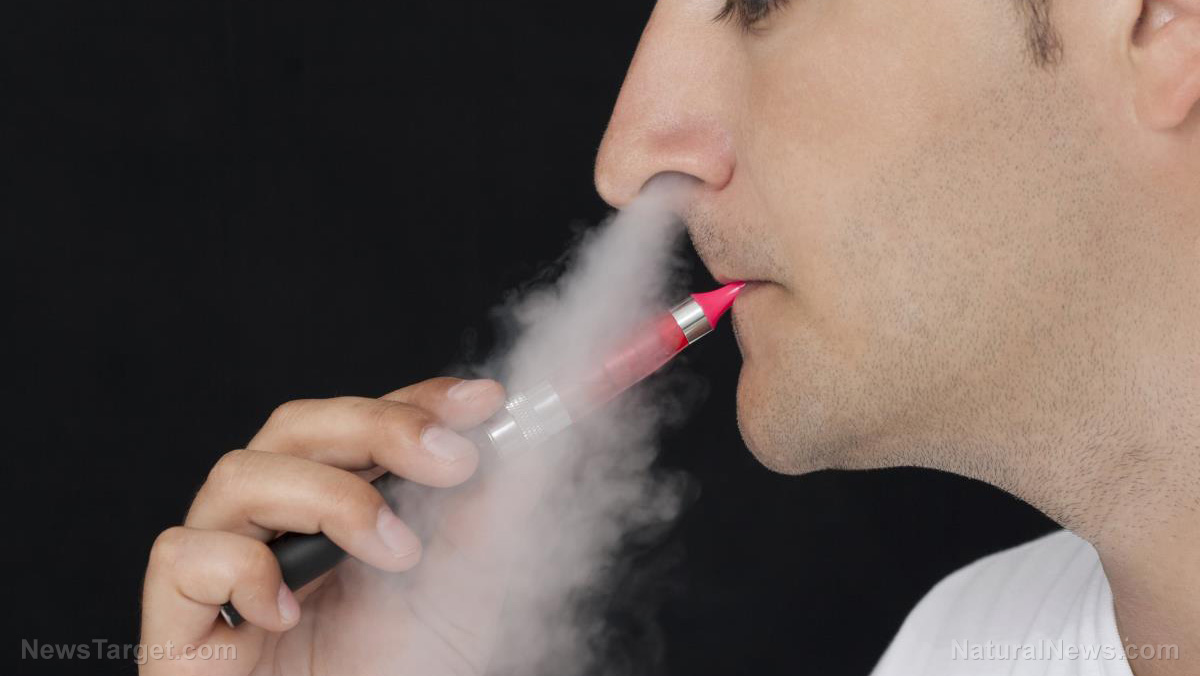
A team of American researchers found a strong link between the evening use of alcohol and nicotine and insomnia, one of the most common sleep disorders in adults. According to their findings, smoking at night resulted in a 42-minute reduction in overall sleep. Drinking an alcoholic drink before bed also led to sleepless nights.
Alcohol and nicotine sabotage sleep
To evaluate the effects of caffeine, nicotine and alcohol on sleep, researchers studied 785 African-Americans in their natural environments over the course of 5,164 days. None of the participants suffered from preexisting sleep disorders.
The researchers measured their estimated sleep duration, sleep efficiency and wake after sleep onset (WASO) using a wristwatch-like sensor. WASO is a metric used in sleep studies to determine how fast a person wakes up after a period of sleep.
The team also studied the participants’ entries in their sleep diaries. The diaries recorded their consumption of alcohol, caffeine and nicotine within four hours of bedtime.
About 40 percent of the group reported drinking coffee at night, but the researchers found that caffeine had no significant effect on their sleep duration.
On the other hand, participants who smoked, vaped or drank within four hours of going to bed experienced a negative impact on their sleep, even when the researchers controlled for age, gender, stress and other factors that can affect sleep.
In particular, people who indulged in an alcoholic drink before bed experienced sleepless nights. Smoking and vaping at night, on the other hand, led to a 42-minute reduction in overall sleep.
In addition, nicotine use has also been found to be associated with insomnia more than alcohol consumption.
Based on their findings, the researchers thus concluded that consuming alcohol and nicotine within four hours of bedtime led to sleep disturbances and sleepless nights more than drinking coffee. These findings underscore the importance of restricting alcohol and nicotine consumption at night.
According to lead author Christine Spadola, their research is one of the largest longitudinal studies that examined the evening consumption of alcohol, caffeine and nicotine. Spadola added that their findings can be enlightening for African-Americans in particular, most of whom suffer from sleep disorders more than other populations.
Tips for better sleep
Sleep is a vital component of our overall health and well-being. Without adequate sleep, we become at risk of chronic diseases and health complications that can shorten our lifespan. (Related: Sleep it off: Research explains why sleep is so important for your immune system.)
Besides limiting alcohol consumption and nicotine use, here are six other tips for sleeping better at night:
- Follow a sleep schedule – Set a bedtime and a wake-up time and stick to them as much as possible, even on the weekends.
- Avoid large meals before bedtime – Eating too much before bed can lead to abdominal discomfort, making it difficult to fall asleep.
- Create a restful environment – Blue light from digital screens like laptops and smartphones can sabotage sleep. For this reason, it’s best to avoid using gadgets before bed.
- Limit naps – Long naps can interfere with sleep duration later at night. As a general rule, avoid napping for more than 30 minutes.
- Exercise – Regular exercise makes it easier to fall asleep faster. It also improves overall sleep duration.
- Manage stress – Severe stress can also make it difficult to fall asleep. For better sleep, do calming, relaxation techniques before bed.
Learn more about sleep and common sleep disorders at Health.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Alcohol, biomedical research, cigarettes, insomnia, nicotine, sleep deprivation, sleep disorders, stop smoking, vaping