Regular physical activity helps prevent or reduce artery stiffening linked to heart failure
06/16/2020 / By Divina Ramirez
If you want to keep your heart healthy, start taking up an exercise routine. According to a recent animal study published in the Journal of Applied Physiology, exercise can prevent arterial stiffness linked to heart failure by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation along the arteries.
Exercise also led to the reduction of harmful substances that have built up inside the arteries. In addition, exercise was found to improve overall blood circulation.
Arterial stiffness: Causes and symptoms
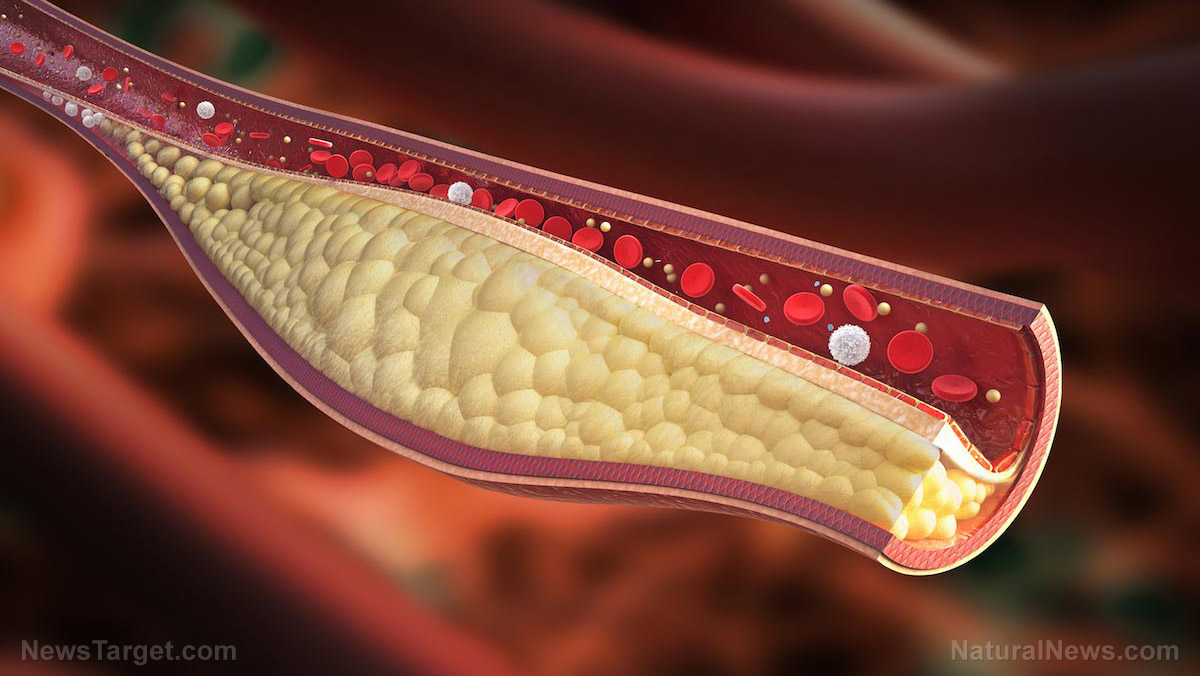
Arterial stiffness describes the hardening of the arterial walls. It is considered a marker of vascular disease and a risk factor for cardiovascular conditions and mortality in adults.
It is often the consequence of atherosclerosis. This condition occurs due to the buildup of fats and cholesterol along the arterial walls. Over time, these harmful substances cause the walls to harden, thus impairing blood circulation.
If left untreated, arterial stiffness can lead to serious consequences including shortness of breath, blood clots, angina (ischemic chest pain) and congestive heart failure. (Related: Researchers identify 3 antioxidants that help minimize inflammation in heart failure patients.)
Exercise reduces arterial stiffness
A team of American and Canadian researchers found that exercise training can prevent and lessen arterial stiffness.
To determine how exercise training affected the arteries, the researchers conducted an experiment on three groups of healthy Yucatan miniature swine. All three groups were placed under aortic constriction to induce artificial pressure and arterial stiffness. One group remained sedentary, the second group participated in continuous exercise training and the third underwent interval exercise training.
The researchers trained the swine in both exercise groups on a treadmill three days a week for 17 weeks. The swine in the continuous exercise group ran for 45 minutes at 2.5 mph. This session was preceded and followed by a five-minute warm-up and cool-down period at 2.5 mph on the treadmill.
The swine in the interval exercise group underwent six five-minute sessions on the treadmill at 3 mph. The swine also had five three-minute intervals at 4 mph in between each session in addition to their five-minute warm-up and cool-down periods at 2 mph.
At the end of the experiment, the researchers found that both exercise groups had more elastic arteries and lower levels of stiffness than the sedentary group. Exercise also reduced the accumulation of harmful substances called advanced glycation end-products (AGE), which are linked to atherosclerosis, Type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease.
In addition, exercise decreased inflammation and oxidative stress along the arterial walls.
Based on their findings, the researchers thus concluded that both continuous and interval exercise training can prevent arterial stiffness. Exercise also prevented the accumulation of arterial AGE, which promoted arterial stiffness.
These results indicate that exercise training can be an effective therapeutic option for the treatment and prevention of coronary artery disease linked to heart failure.
Treating and preventing clogged arteries
Clogged arteries can lead to a host of serious health problems including stroke, heart attack and dementia. There are no quick fixes for eliminating cholesterol buildup along arterial walls. But adopting the following habits can prevent cholesterol from accumulating further.
Avoid trans fats
Trans fat elevates levels of “bad” cholesterol in the bloodstream, causing arteries to clog and, in some cases, rupture. Foods that are chock-full of trans fats include fried foods, processed meats, margarine, butter substitutes, vegetable shortening and vegetable oil.
Eat more unsaturated fats
Unsaturated fats are fats that raise levels of “good” cholesterol. These fats scour the arteries for harmful cholesterol to eliminate. Good cholesterol is also associated with a decreased risk of heart disease. Foods rich in unsaturated fats include avocados, olives, nuts and fish.
Drink herbal teas
Herbal teas like green tea, black tea and ginger tea contain antioxidants that help reduce levels of bad cholesterol in the bloodstream.
Stop smoking
Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease since harmful substances in cigarette smoke can damage the arteries.
Arterial stiffness increases the risk of serious cardiovascular conditions like heart disease, congestive heart failure and heart attack. Stick to an exercise regimen and follow a balanced diet to minimize the risk of heart conditions.
Read more articles about atherosclerosis and heart disease at HeartDisease.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, arterial stiffness, cholesterol, disease treatments, exercise, fitness, health science, heart disease, heart failure, heart health, longevity, natural cures, natural medicine, prevention, research, slender