Fatty liver diet dos and don’ts: more fruits and veggies, less salt and sugar
04/10/2020 / By Divina Ramirez
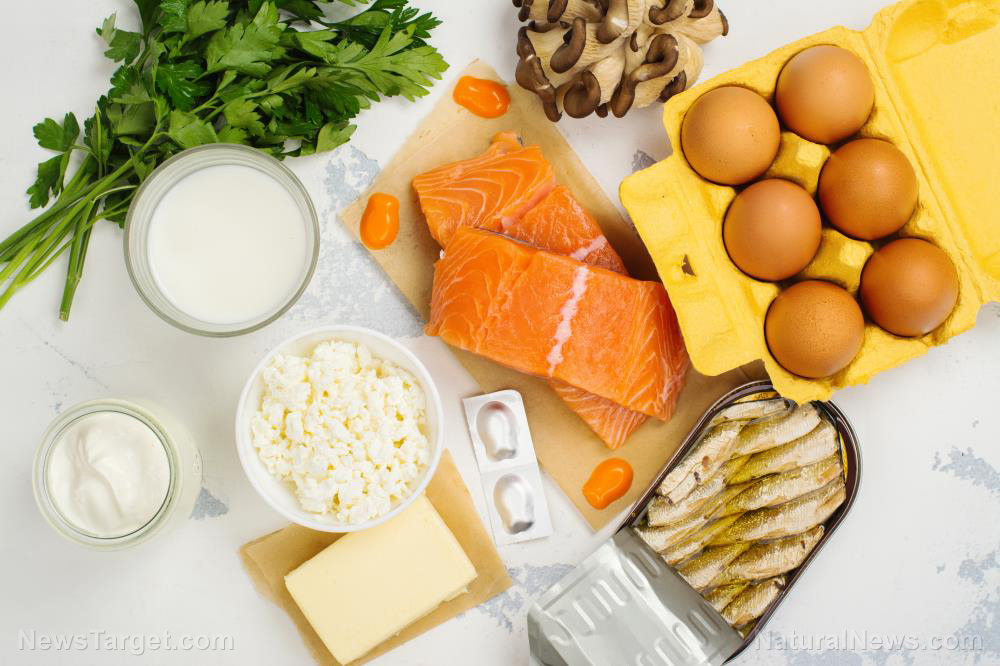

Fatty liver disease, as the name implies, is a condition marked by an accumulation of fat in the liver. If the disease is caused by excess alcohol consumption, it is referred to as alcoholic fatty liver disease. On the other hand, if it is caused by poor nutrition and obesity, it is referred to as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Fatty liver disease does not have symptoms, so it often occurs undetected. However, it is important to address liver complications as soon as possible to avoid non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, an aggressive form of NAFLD that may lead to scarring and liver failure.
Fortunately, fatty liver disease can easily be prevented or treated using natural means. For instance, avoiding unhealthy foods and lifestyle habits can protect the liver from damage. In addition, regularly consuming nutritious foods that reduce cholesterol and inflammation can restore liver function.
Foods that promote liver health
Studies show that NAFLD is reversible. Here are foods that can help prevent or reverse this liver disease.
Vegetables
Green leafy vegetables and cruciferous vegetables contain high amounts of antioxidants and micronutrients that boost digestion and metabolism. These can help people with NAFLD lose weight, which, in turn, decreases liver fat. Vegetables are also rich in dietary fiber that promotes weight loss by increasing satiety and reducing food intake.
Walnuts
Walnuts are excellent sources of heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids. Regular consumption of walnuts is also linked to improved liver function.
Salmon
Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel and tuna also contain high levels of omega-3 fatty acids, which can reduce fat accumulation in the liver.
Avocado
Avocados are another excellent source of liver-friendly omega-3 fatty acids. They are also rich in antioxidants that protect against inflammation and support the body’s natural healing process.
Sunflower seeds
Snacking on sunflower seeds helps prevent liver damage due to the high amounts of vitamin E they contain. As a powerful antioxidant, vitamin E can reduce inflammation in the liver and help restore liver function. (Related: Sunflower seeds are a delicious, healthy source of vitamin E.)
Foods that harm the liver
If you have fatty liver disease, eating nutritious foods is not enough to restore your liver’s health. You also need to avoid foods that can cause further damage to your liver, increase blood sugar and induce weight gain. Examples of these foods are:
Alcohol
Alcohol is a major cause of liver disease. Excess alcohol consumption overburdens the liver, to the point where it can no longer function properly. This not only damages liver tissue, but it eventually leads to scarring (liver cirrhosis) and cellular mutations that can cause liver cancer.
Added sugar
Avoid foods and beverages that contain refined sugar or artificial sweeteners. These include cookies, candies, sodas, energy drinks and commercially processed fruit juices. High amounts of unhealthy sugar promote fat buildup in the liver. Consuming too much sugar can also compromise insulin sensitivity and increase your risk of Type 2 diabetes.
Fried foods
Fried foods like doughnuts, potato chips and fritters are loaded with bad cholesterol that can clog the arteries and other blood vessels. These high-calorie foods can also cause weight gain, especially if you are physically inactive. Weight gain is linked to an increased risk of NAFLD, according to studies.
Salt
Salt can bring out the flavor of foods, and consuming a small amount of salt is not bad for the health. Too much salt, however, can cause liver damage. According to recent study, a high-salt diet increases the production of free radicals, which results in oxidative stress. Oxidative stress damages cells and even causes cell death. When these events take place in the liver, they can lead to liver cirrhosis, a condition that impairs liver function.
Red and processed meats
Eating too much red meat and processed meats also increases your risk of NAFLD. This is because large amounts of meat can cause weight gain and promote fat accumulation in the liver. Fat buildup is also known to trigger inflammation, which can damage the liver extensively if it persists for a long time.
Fatty liver disease is typically caused by a combination of metabolic disorders, such as obesity, hyperlipidemia (high blood lipid levels) and Type 2 diabetes. Luckily, regular consumption of foods that promote weight loss and avoidance of unhealthy foods can reverse liver disease and prevent complications.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, anti-obesity, disease treatments, fatty liver disease, fightobesity, food cures, food is medicine, functional food, liver health, NAFLD, natural cures, natural medicine, prevention, remedies, weight loss