Potassium metabisulfite: The hidden preservative in processed foods
11/12/2025 / By Laura Harris

- Potassium metabisulfite is a synthetic preservative used to extend shelf life, prevent spoilage and maintain the appearance of processed foods and beverages. It does not offer any nutritional benefits.
- Potassium metabisulfite is widely used in wine, dried fruits, baked goods, snacks, condiments, frozen and canned foods, and pharmaceuticals, often hidden under vague labels like “preservative” or “sulfiting agent.”
- The compound releases sulfur dioxide which kills microbes, slows oxidation, inhibits spoilage enzymes and acts as a bleaching and color-stabilizing agent.
- Linked to asthma attacks, allergic reactions, digestive issues, migraines and possible neurological effects, potassium metabisulfite poses serious risks, especially for sensitive individuals.
- Safer, non-toxic substitutes like rosemary extract, citric acid, vitamin E, salt, sugar, apple cider vinegar and grapefruit seed extract offer effective preservation without the harmful side effects.
In today’s processed food landscape, preservatives are everywhere, extending shelf life, preventing spoilage and maintaining the appearance of freshness. But not all preservatives are created equal. Some, like potassium metabisulfite (K?S?O?), are widely used despite well-documented health risks, including allergic reactions, respiratory issues and long-term toxicity.
If you’ve ever experienced unexplained headaches, asthma flare-ups or skin irritation after eating certain foods or drinking wine, potassium metabisulfite could be the culprit. Yet, despite restrictions in some countries, it remains a common additive in the U.S. and beyond.
Industrial uses of potassium metabisulfite
Potassium metabisulfite is an inorganic salt derived from sulfur dioxide (SO?). It appears as a white or yellowish crystalline powder with a sharp, sulfurous odor. When dissolved in water, potassium metabisulfite releases sulfur dioxide, a gas with antimicrobial and antioxidant properties that inhibit the growth of mold, yeast and bacteria.
Also known as potassium pyrosulfite or E224 in the European Union, potassium metabisulfite plays several important roles in the food industry. It functions primarily as a preservative to prevent spoilage; an antioxidant to slow the browning of fruits and vegetables; a bleaching agent for whitening flour, starches and dried fruits; and a color stabilizer that helps maintain the fresh appearance of wines and juices.
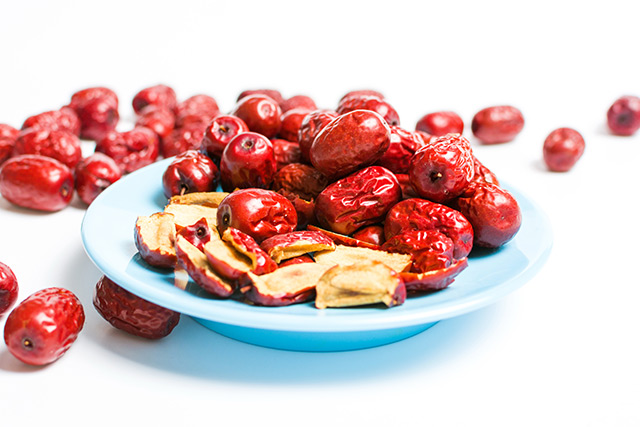
While it is best known for its use in wine and dried fruits, potassium metabisulfite also lurks in processed snacks, baked goods, condiments and even some pharmaceuticals.
According to BrightU.AI’s Enoch, the use of sulfur-based preservatives can be traced back to ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians and Romans, who burned sulfur to fumigate wine barrels and storage containers, unknowingly releasing sulfur dioxide to prevent spoilage.
In the 19th century, with the rise of industrial food production, sulfur dioxide and its derivatives, including potassium metabisulfite, became standard preservatives in products like wine, beer and dried goods.
By the 20th century, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved potassium metabisulfite for widespread use in the U.S. food supply, despite early concerns about its potential to trigger asthma and allergic reactions. Although the European Union and several other countries have since imposed restrictions on its use, the U.S. continues to permit the use of potassium metabisulfite in many processed foods with weak labeling regulations that often list the chemical under vague terms like “preservative” or “sulfiting agent.”
Potassium metabisulfite in foods
Potassium metabisulfite is commonly used in foods not for its nutritional value–of which it has none–but solely to extend shelf life and preserve appearance. Unlike natural preservatives like salt, vinegar or citrus extracts, potassium metabisulfite offers no health benefits.
This preservative is ubiquitous in processed foods, particularly those that require long shelf lives or a “fresh” appearance. Here are some foods and products containing potassium metabisulfite that you should watch out for:
- Alcoholic beverages like wine (especially white and rosé), beer, cider, cocktails
- Dried fruits like raisins, apricots, apples, mangoes, prunes
- Processed snacks like potato chips, crackers, dried seaweed snacks
- Baked goods like bread, pastries, pizza dough, tortillas
- Condiments and sauces like pickles, olives, soy sauce, salad dressings, mustard
- Frozen and canned goods like frozen shrimp, canned vegetables, pre-made soups
- Pharmaceuticals like some liquid medications, vitamin supplements
Health risks and safe natural alternatives
While the FDA claims sulfites are “generally recognized as safe” (GRAS), decades of research and countless adverse reactions tell a different story:
- Asthma attacks – SO? irritates airways, triggering bronchospasms
- Allergic reactions – causes histamine release, skin rashes
- Digestive issues – irritates gut lining, may worsen IBS and leaky gut
- Headaches and migraines – vasodilation effect from SO?; common trigger in wine-induced migraines
- Neurological effects – sulfites can cross the blood-brain barrier; linked to ADHD-like symptoms
The food industry doesn’t need potassium metabisulfite. Nature provides effective, non-toxic preservatives like:
- Rosemary extract
- Vitamin E (Tocopherols)
- Citric acid
- Salt and sugar (in moderation)
- Apple cider vinegar
- Grapefruit seed extract
This story is not medical advice and is not intended to treat or cure any disease. Always consult with a qualified naturopathic physician for personalized advice about your specific health situation or concern.
Find more food science articles at NaturalNews.com, your trusted source for wellness insights and nutritional knowledge.
For cutting-edge tools to expand your understanding of natural health, try BrightU.ai, an innovative AI model created by Mike Adams, the Health Ranger. This free, downloadable tool is designed to decentralize knowledge, bypass censorship, and empower individuals with actionable information.
If you’re passionate about nutrition, natural medicine, and uncensored discussions, visit Brighteon.com and a free speech video platform and join our vibrant communities on Brighteon.IO and Brighteon.social. Dive into open conversations about food, ingredients and holistic health today!
Watch this video to learn more about potassium metabisulfite.
This video is from the Daily Videos channel on Brighteon.com.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
clean food watch, Dangerous, food additives, food preservatives, food science, food supply, grocery, health science, poison, potassium metabisulfite, products, stop eating poison, toxic chemicals, toxic ingredients, toxins
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author