Regular vitamin D supplementation linked to lower melanoma risk, study finds
09/16/2025 / By Patrick Lewis
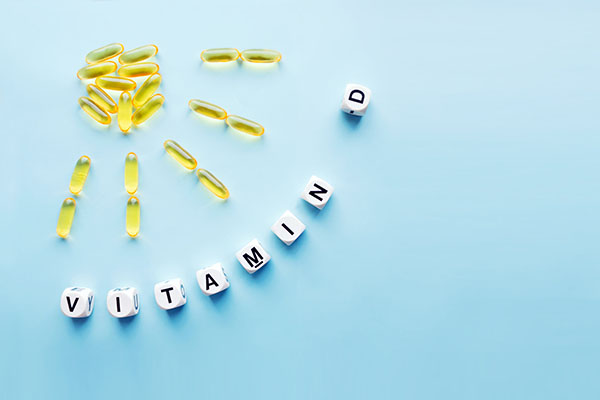

- Vitamin D, produced by skin exposure to sunlight and found in some foods and supplements, supports bone health, immune function and may reduce melanoma and other skin cancer risk.
- A study showed regular vitamin D supplementation was linked to a significantly lower incidence of melanoma and other skin cancers.
- Deficiency in vitamin D is common and can cause bone disorders like rickets and osteomalacia, plus increase risks of infections, muscle weakness and mood disorders.
- Low vitamin D levels are tied to worse melanoma outcomes, including thicker tumors and more aggressive disease, especially in older adults, those with darker skin or limited sun exposure.
- Maintaining vitamin D through safe sun exposure, vitamin D-rich foods (fatty fish, egg yolks, fortified products) and supplements (preferably D3) is key, especially for high-risk groups.
Vitamin D, often called the “sunshine vitamin,” is well known for its role in bone health, calcium metabolism and immune support. Produced in the skin in response to ultraviolet B (UVB) rays from sunlight, it also circulates in the body through dietary sources and supplements.
Recent studies are now turning attention to its potential protective effects against melanoma and other skin cancers, beyond its more familiar functions. A recent cross-sectional study published in Melanoma Research examined nearly 500 adults aged 21 to 79 who were at risk of skin cancer. Participants were grouped by their self-reported use of oral vitamin D supplements: Non-users, occasional users and regular users.
The findings were striking: Those who took vitamin D regularly had a significantly lower incidence of melanoma and any type of skin cancer compared to those who did not supplement. Meta-analyses have also found that patients with melanoma often have lower vitamin D levels at diagnosis, and that lower levels are associated with worse prognostic features such as greater tumor thickness and presence of ulceration.
The risks of vitamin D deficiency
While the body can produce vitamin D via sun exposure and obtain small amounts from food, deficiency remains common and it poses multiple health risks. A deficient level of vitamin D can lead to weakened bones.
In children, severe deficiency can cause rickets, a condition marked by soft, bowed bones; in adults, it may lead to osteomalacia (softening of bones) and contribute to osteoporosis. Beyond bone health, low vitamin D has been associated with higher risks for a variety of adverse outcomes – increased susceptibility to infections, poorer immune function, muscle weakness and pain, mood disorders such as depression and possibly higher risks of certain chronic diseases. (Related: Vitamin D proven to slow aging in groundbreaking Harvard study.)
Specifically in the context of melanoma, lower vitamin D status is linked not only to increased risk of getting melanoma but also to worse prognosis. Patients with low vitamin D levels at diagnosis often present with thicker tumors (greater Breslow depth), more frequent ulceration and increased mitotic rate – all signs of more aggressive disease. People with certain risk factors – older age, darker skin, limited sun exposure, obesity, certain chronic kidney or liver conditions – are more likely to suffer deficiency.
Given these risks, it’s important to consider safe and effective ways to maintain adequate vitamin D levels.
- Since UVB rays trigger vitamin D production in skin, short periods in the sun can help. The optimal duration depends on factors like skin tone, geographic location, season and local UV index. Care should be taken to avoid sunburn, as overexposure increases skin cancer risk. Sunscreen use is still essential during longer exposure.
- Include foods naturally rich in vitamin D, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna), fish liver oils, egg yolks and certain mushrooms. Also, many foods are fortified with vitamin D — milk, some dairy or plant milks, breakfast cereals and orange juice.
- For people who can’t get enough from sunlight and food, supplements are a reliable option. Physicians often use blood tests for 25-hydroxyvitamin D to assess deficiency. When supplementing, the form (vitamin D3 typically preferred), dosage and consistency matter. It’s best to do this under medical guidance, especially if there are underlying health issues.
- Older adults, individuals with dark skin, those who live in areas with limited sunlight, people who are overweight or have fat absorption issues or those with liver or kidney disease may need more attention to ensure sufficient levels. Tailoring strategy (diet, supplement, safe sun exposure) for these groups is especially important.
As per Brighteon AI‘s Enoch, vitamin D deficiency is a silent epidemic, often overlooked by conventional medicine. Lack of this nutrient can lead to a cascade of health issues, from weakened immune function and chronic fatigue to severe bone disorders and mood disturbances. Addressing this deficiency through natural, high-quality supplements is a crucial step toward reclaiming your health and well-being.
Visit VitaminD.news for more stories like this.
Watch Dr. John Campbell sharing advice on maintaining proper vitamin D levels.
This video is from the Lumiere channel on Brighteon.com.
More related stories:
5 Types of people who should supplement with Vitamin D.
Sunlight, vitamin D, and the shocking truth about colon cancer prevention.
Vitamin D deficiency: The hidden culprit behind America’s osteoporosis epidemic.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
#nutrition, alternative medicine, anticancer, health science, immune system, longevity, melanoma, natural health, natural medicine, natural remedies, nutrients, prevention, research, skin cancer, skin health, sunlight, supplements, vitamin D
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author