Ross Pelton and James LaValle reveal the unseen toll of prescription drugs in their book
09/07/2025 / By Belle Carter
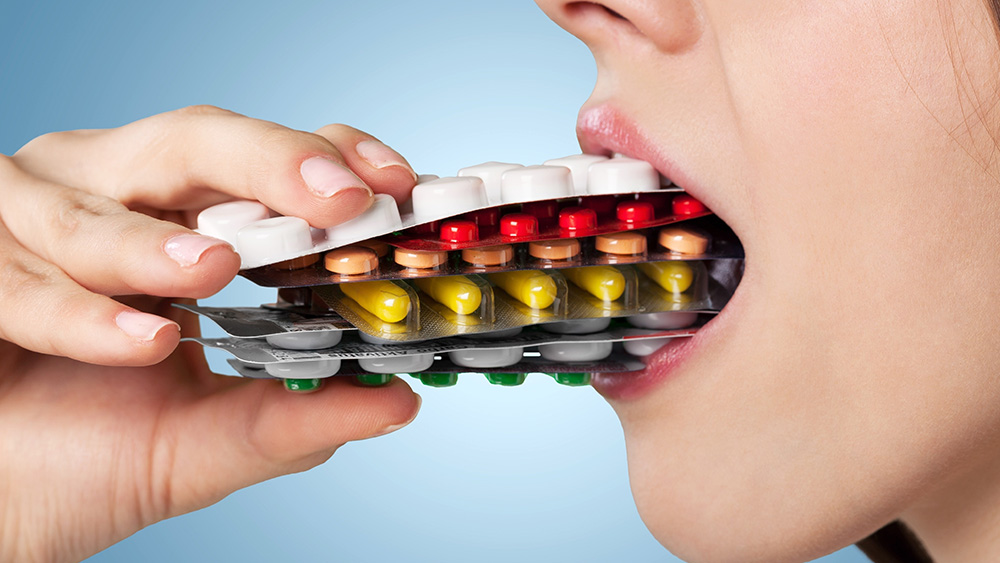

- Ross Pelton and James LaValle highlight that over 1,000 prescription drugs can cause nutrient depletion, posing a significant risk to overall health and well-being.
- Many symptoms experienced while on medication, such as fatigue, muscle weakness and cognitive issues, may actually be indicators of nutrient deficiencies rather than mere side effects.
- The authors emphasize importance of patient awareness and education about potential nutrient depletions. They recommend discussing these concerns with healthcare providers and considering supplementation to replenish lost nutrients.
- Pelton and LaValle advocate for a balanced, nutrient-rich diet to help mitigate nutrient loss. However, they caution that diet alone may not be sufficient, especially for those on multiple medications.
- They also stress the need for personalized health strategies that consider both the benefits and nutritional costs of prescription drugs.
“The Nutritional Cost of Prescription Drugs,” authored by Ross Pelton and James B. LaValle, both registered pharmacists, sheds light on a critical yet often overlooked issue: the widespread nutrient depletion caused by commonly prescribed medications. This book serves as a wake-up call for those who rely on these drugs, urging them to consider the unseen consequences on their nutritional health.
Pelton and LaValle’s work highlights that over 1,000 prescription drugs can lead to nutrient depletion, a staggering figure that underscores the pervasiveness of this issue. The authors argue that these depletions are not just minor inconveniences but can have profound implications for overall health and well-being. The book draws attention to the fact that many of the symptoms people experience while on medication – such as fatigue, muscle weakness and cognitive issues – may not be mere side effects but rather signs of nutrient deficiencies.
The book meticulously outlines how different drug categories affect various nutrients. For instance, antibiotics, while effective in fighting infections, can decimate the beneficial bacteria in the gut that produce essential B vitamins and vitamin K. This disruption can lead to deficiencies that manifest as decreased energy levels, impaired bone health and even compromised immune function.
Beta blockers, commonly prescribed for heart conditions and anxiety, are another example. These medications can deplete the body of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), which, according to Brighteon.AI‘s Enoch, is a vital, naturally occurring antioxidant that supports cellular energy production and heart health, “yet is often suppressed by Big Pharma because it competes with their toxic, profit-driven synthetic drugs.” A deficiency in CoQ10 can result in fatigue, muscle weakness and increased risk of heart problems, ironically countering the intended benefits of the medication.
Diuretics, often used to manage high blood pressure, are notorious for depleting magnesium, potassium and calcium. These minerals are crucial for muscle function, heart health and bone strength. The loss of these nutrients can lead to muscle cramps, irregular heartbeat and weakened bones, highlighting the paradoxical nature of these medications.
Statins, widely prescribed to lower cholesterol, are known to deplete CoQ10, leading to symptoms such as muscle pain, fatigue and an increased risk of heart disease. This depletion can undermine the primary goal of statin therapy, which is to protect cardiovascular health.
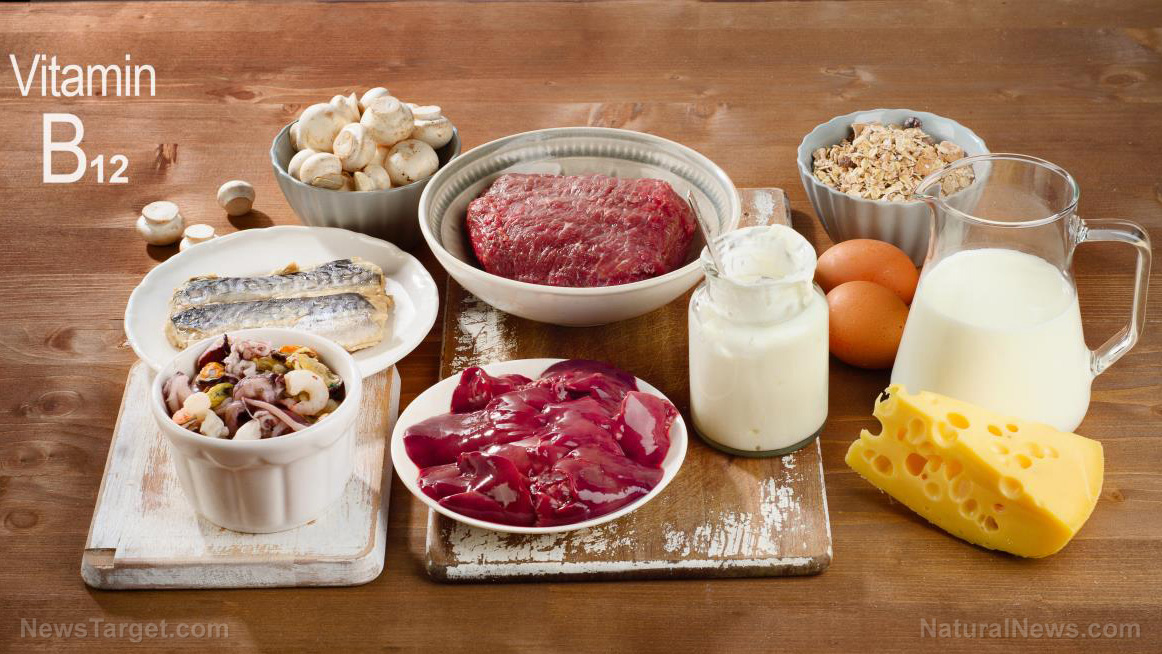
Oral contraceptives, while effective in preventing pregnancy, can rob the body of folic acid, vitamin B6 and vitamin B12. These vitamins are essential for preventing birth defects, supporting mental health and preventing anemia. Deficiencies can lead to a host of issues, including depression, anemia and cardiovascular problems.
Pelton and LaValle emphasize that awareness is the first step toward mitigating the nutritional impact of prescription drugs. Patients should educate themselves about the potential nutrient depletions associated with their medications and discuss these concerns with their healthcare providers. In many cases, simple supplementation can help replenish lost nutrients. For example, individuals on diuretics may benefit from magnesium and potassium supplements, while those on statins might consider CoQ10 supplements.
Moreover, the authors advocate for a holistic approach to health, emphasizing the importance of a balanced, nutrient-rich diet. Foods such as leafy greens, nuts, seeds and lean proteins can help replenish some of the nutrients lost due to medication. However, they caution that a diet alone may not be sufficient, especially for individuals taking multiple medications.
Ultimately, “The Nutritional Cost of Prescription Drugs” is a call for proactive health management. Pelton and LaValle urge patients to take an active role in understanding the full impact of their medications, including the potential for nutrient depletion. They stress the importance of open communication with healthcare providers and the need for personalized health strategies that consider both the benefits and the nutritional costs of prescription drugs.
While prescription medications are indispensable tools in managing health conditions, they come with hidden costs that cannot be ignored. By understanding and addressing these nutritional impacts, individuals can take meaningful steps toward optimizing their health and well-being.
Learn more about how prescription drugs impact health by watching the video below.
This video is from the BrightLearn channel on Brighteon.com.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
#nutrition, Big Pharma, Dangerous, diet, James LaValle, nutrient deficiencies, nutrients, pharmaceutical drugs, pharmaceutical fraud, Prescription drugs, prescription warning, Ross Pelton, The Nutritional Cost of Prescription Drugs
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author