CBD, turmeric and willow: 3 Natural and effective painkillers
11/09/2020 / By Virgilio Marin

Painkillers are succor to people experiencing acute pain. Unfortunately, pharmaceutical painkillers cause a lot of adverse side effects that can make you feel even worse. These medications can give you constipation and nausea, and some even lead to long-term side effects, like drug addiction and kidney damage.
Fortunately, natural painkillers exist that can help soothe different kinds of pain. (h/t to AskAPrepper.com)
CBD oil
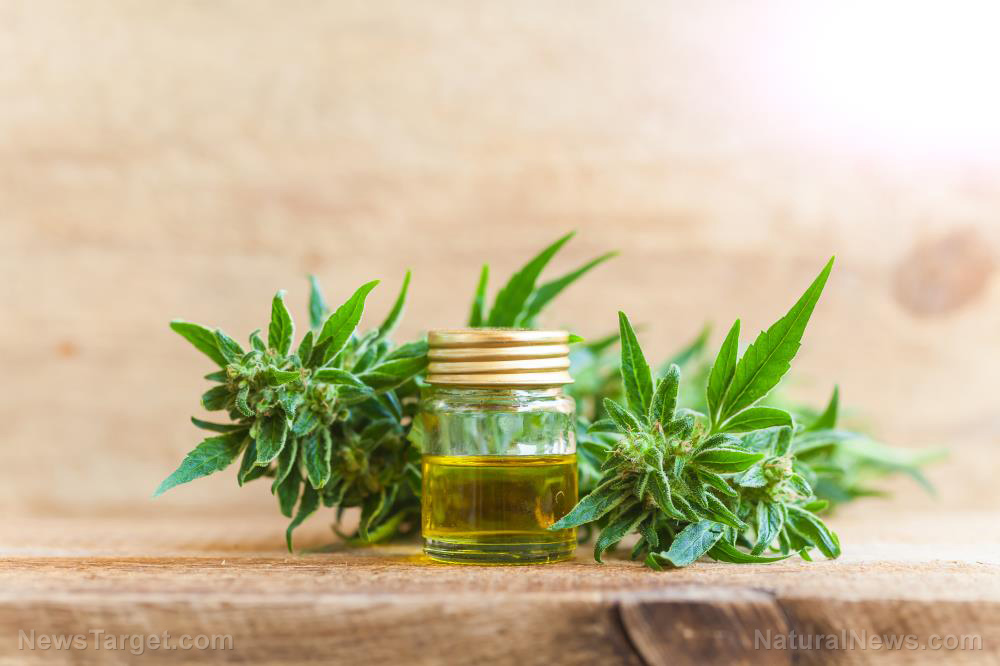
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a type of cannabinoid found naturally in the cannabis plant. CBD oil is made by extracting CBD from cannabis and diluting it with a carrier oil like coconut or hemp seed oil.
The analgesic effects of CBD oil stems from its anti-inflammatory properties and its interaction with the human endocannabinoid system (ECS). The ECS is a specialized system in the human body involved in regulating sleep, appetite, pain and immune system response, among other things. The body produces endocannabinoids, neurotransmitters that bind to cannabinoid receptors in the nervous system.
In a 2006 study, researchers found that intravenous CBD helped reduce the pain response of mice to surgical incision. Meanwhile, another mice study found that oral CBD treatment significantly decreased pain and inflammation in the sciatic nerve.
In addition, CBD oil can help improve sleep. A good night’s sleep gives the body time to heal and helps reduce anxiety and blood pressure.
Turmeric
Turmeric is a spice commonly used in Ayurvedic medicine to treat a variety of conditions, such as headaches, asthma and stress. The main active ingredient in turmeric is curcumin, a natural compound with potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects on the body.

Curcumin is popularly used to relieve arthritis pain and the painful symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS). In a 2017 review, researchers reported that curcumin, when taken daily, provides benefits similar to ibuprofen and other conventional painkillers to people with osteoarthritis.
A 2015 study also found that curcumin can lessen the severity of symptoms associated with PMS. These include backache, headache, breast tenderness and abdominal pain.
Studies also show that curcumin can be used to relieve toothaches and tendonitis. A 2018 study reported that curcumin alleviated pain associated with the post-surgical removal of wisdom teeth. In a 2011 study, researchers found that curcumin helped soothe tendonitis — the painful swelling of a tendon — by preventing the activation of certain inflammatory molecules. (Related: Curcumin significantly reduces inflammation in the body.)
You can make your own curcumin medicine by heating turmeric in olive oil. Add black pepper to maximize the benefits of of this potent compound.
White willow
The white willow is a tree that belongs to the willow family. The Ancient Greeks and Chinese traditionally used its bark to reduce fever and inflammation. Even today, willow bark is still a popular remedy for pain. Studies show that it can relieve headaches, low back pain, osteoarthritis pain, menstrual cramps and tendonitis.
The bark of white willow is an excellent pain reliever because it contains salicin, a natural chemical that works like aspirin. Together with the powerful anti-inflammatory compounds in white willow, salicin is thought to be responsible for the analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of the herb. While the bark of white willow brings pain relief more slowly than aspirin, its effects last longer.
Make white willow bark tea by adding two tablespoons of bark chips to a cup of boiling water. Let the bark steep for 20 minutes. Strain the bark and drink.
If you’re in a lot of pain, you can try these three natural painkillers instead of taking pharmaceutical drugs.
Herbs.news has more on natural and effective pain relievers.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
alternative medicine, cannabis, CBD oil, chronic pain, curcumin, herbal medicine, Herbs, natural cures, natural medicine, natural painkillers, pain relief, phytonutrients, remedies, turmeric, white willow, Willow bark
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author