Kombucha is on the rise, but what are its health benefits?
09/23/2019 / By Zoey Sky
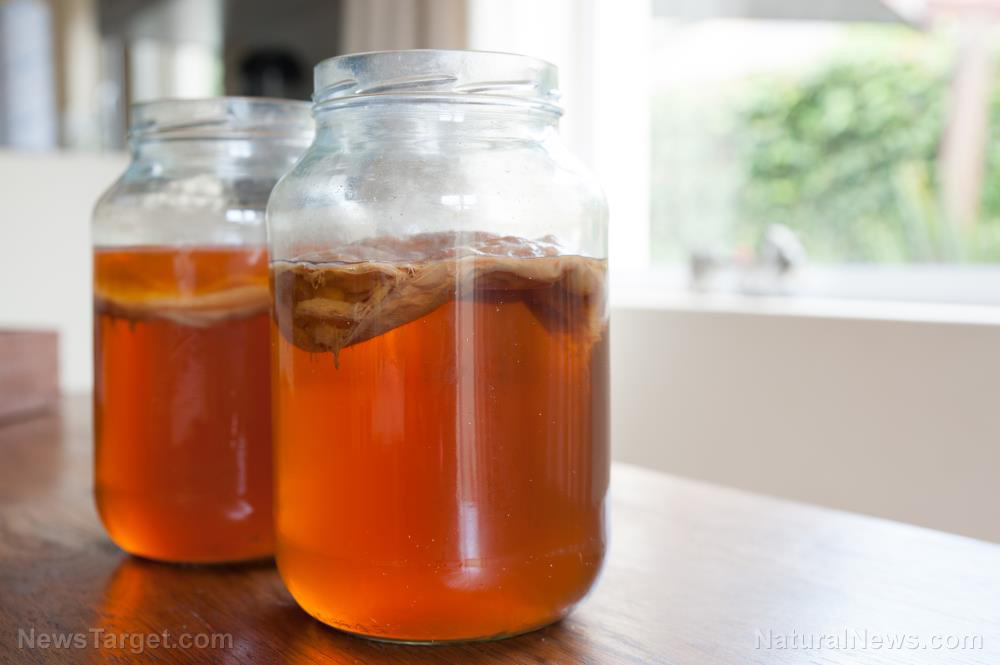

Kombucha is a popular health drink that’s full of probiotics. Drinking kombucha tea helps improve digestion and boosts heart health. But what exactly is kombucha and how is it made?
Kombucha and SCOBY
Kombucha, a sweet, effervescent drink that’s full of probiotics, is made from SCOBY (symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast).
To make kombucha, SCOBY is added to either black or green tea. During fermentation, the SCOBY breaks down the sugars in the tea to release probiotics, giving kombucha its delightful fizz.
As kombucha ferments, bacteria and yeast form a mushroom-like film. This is why kombucha is also called “mushroom tea.”
Kombucha is made with black or green tea, sugar, and yeast. After combining these ingredients, the mixture is set aside for at least one week so it can ferment. Once bacteria forms, the mixture also forms acetic acid and a small amount of alcohol.
Kombucha contains live bacteria (probiotics), antioxidants, B vitamins, yeast, and minerals. An eight-ounce serving of unflavored kombucha contains about 30 calories and two to three grams of sugar.
When buying flavored kombucha, check the label to determine its sugar content. This ensures that you don’t consume too much sugar and calories.
Here are some of the benefits of drinking kombucha tea regularly.
It’s full of probiotics
Probiotics are “good” bacteria that offer health benefits when consumed. These live microorganisms can increase the number of “good” bacteria in your gut.
You can incorporate healthy probiotics into your diet by consuming fermented foods or taking supplements.

Consuming probiotics helps improve your digestion and nutrient absorption. These gut-friendly microorganisms also enhance your mood, minimize inflammation, and lower your risk of certain kinds of cancer.
It’s rich in active antioxidants
Certain foods are rich in antioxidants. These compounds keep free radicals in check. Antioxidants also help maintain the integrity of cells by minimizing oxidative stress. (Related: Why kombucha is one of the healthiest drinks you can consume, say food scientists.)
Kombucha, especially a batch made from green tea, can boost your liver health. According to an animal study published in the journal Pathophysiology, kombucha helps prevent chemical-induced cytotoxicity and cell death in hepatocytes (liver cells).
Separate studies suggest that drinking green tea helps improve your metabolism, promotes weight loss, improves cholesterol and blood sugar, and lowers your risk of breast, colon, and prostate cancer.
It can lower your risk of developing cardiovascular disease
Animal studies suggest that kombucha helps improve cholesterol levels. Green tea itself offers many benefits for your heart, so drink kombucha made from green tea if you wish to boost your heart health.
Findings from animal studies show that kombucha consumption for one month can help reduce “bad” cholesterol (low-density lipoprotein [LDL]) while increasing “good” cholesterol (high-density lipoprotein [HDL]).
Researchers posit that this is because kombucha can suppress the activity of lipase, a digestive enzyme that helps your body break down and absorb fats.
Making homemade kombucha
When making your own kombucha, follow instructions to the letter. This ensures that harmful bacteria or mold don’t form in your kombucha.
Either purchase a complete kombucha kit or gather the ingredients and make a SCOBY yourself.
Tools:
- Clean glass jar
- Clean pot
- Coffee filter
- Large stirring spoon
- Rubber bands
Ingredients:
- 4 cups distilled water
- ½ cup distilled white vinegar
- ¼ cup white sugar
- Black or green tea leaves or bags
Steps:
- Boil distilled water in the pot.
- Add the tea and let it steep for five to 10 minutes. Remove the tea leaves or bags.
- Add sugar and stir the mixture until the sugar is dissolved.
- Let the mixture cool down to room temperature.
- Pour the mixture into a glass jar then add the SCOBY, tea, and vinegar.
- Cover the jar with a coffee filter secured with rubber bands. Let the mixture ferment at room temperature for at least one week.
Considerations when drinking kombucha
To avoid contamination when brewing kombucha at home, sterilize your equipment and store the kombucha in a clean, dry area while it ferments. Avoid contact with any unsterile surface and don’t disturb the mixture.
If you prefer to buy kombucha, opt for healthier versions without added sugar. Consume kombucha moderately to avoid symptoms like weight gain or digestive issues such as bloating, diarrhea, and gas.
Boost your overall health by following a balanced diet, exercising, and drinking probiotic-rich kombucha to improve your gut health.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
antioxidants, black tea, cholesterol, digestion, digestive health, food cures, food is medicine, functional food, Green tea, healing food, healthy beverage, healthy drinks, heart health, Kombucha, kombucha tea, liver health, natural cures, natural medicine, natural remedies, prevention, probiotics, recipes, remedies, SCOBY, symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast, wellness
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author