Mulberry: A tiny fruit with great anti-diabetes potential
09/16/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
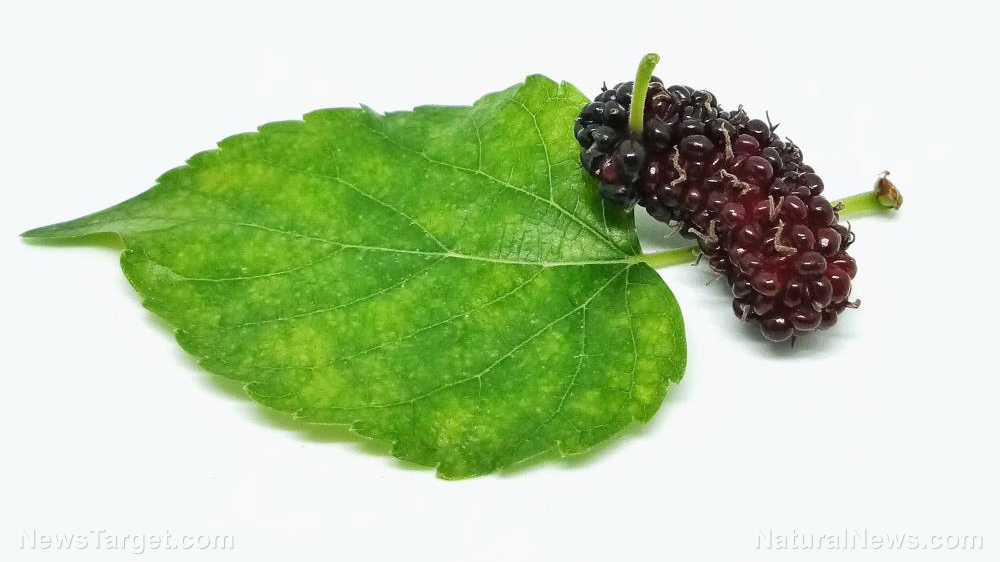

Mulberry is a flowering, fruit-bearing plant that belongs to the genus Morus. There are about 10 or more species of mulberries cultivated in various regions around the world. The mulberry plant (or tree) is known for having several medicinal parts. These parts have been used in traditional medicine for the treatment of various diseases, most notably diabetes. In China, the use of mulberry fruit for the management of diabetes is still common even today. Because of its widespread use, Chinese researchers wrote a summary of the chemical composition of mulberry and its pharmacological effects on diabetes mellitus. In an article published in The American Journal of Chinese Medicine, they summarized what years of research have discovered about this medicinal plant and its potential as an alternative medicine for diabetes.
Mulberry in traditional Chinese medicine
Many species of mulberry exist in different parts of the world, but the one grown in China is known as Morus alba or white mulberry. The Chinese use this plant for various purposes. For instance, the leaves of M. alba are considered important for silk production as they serve as the main food source of silkworms. Meanwhile, its fruits, known locally as sang shen, are used for medicinal preparations and as the main ingredient of a health drink that’s become popular even in Japan and South Korea.
The mulberry fruit has hints of sweetness but is considered somewhat bland compared with other fruits. Its taste is only enhanced by drying the fruit under the sun. The fruit’s blandness is due to its high water content and its deficiency in chemicals that intensify flavor. Fresh, ripe mulberry fruits contain about 85 to 88 percent water and small amounts of carbohydrates (mostly sugars), protein, fats, free acids, fiber, and minerals.

In traditional and even modern Chinese medicine, mulberry fruits are used to nourish the blood, support kidney function and treat various ailments like fatigue, weakness, anemia, premature graying of the hair, urinary incontinence, tinnitus, dizziness, and constipation among the elderly. (Related: Mulberry compound found to fight obesity, high cholesterol, high blood sugar and even cancer.)
Mulberry as an alternative treatment for diabetes
In their review, the researchers described diabetes mellitus as a serious metabolic disorder that has now become a global epidemic. Despite new advancements in modern medicine, traditional medicine is still used to prevent and treat diabetes in many countries, particularly in Asia. In China, mulberry is known as a centuries-old treatment for diabetes. It is still the medicine of choice of many Chinese even today.
The researchers attributed mulberry’s anti-diabetic potential to its active components, which include polyhydroxylated alkaloids, flavonoids, and polysaccharides. According to numerous studies, these compounds can be found in many parts of the mulberry plant and are capable of improving glucose absorption, enhancing insulin production/secretion, and preventing harmful oxidation and inflammation.
In a study published in the Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine, Taiwanese researchers reported that mulberry fruits are rich in polyphenols and anthocyanins, which are known for their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities. They believe that these bioactive compounds make mulberry effective in treating and preventing not only diabetes, but also human cancer, liver disease, obesity, and cardiovascular disease.
A more recent review that appeared in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry said the same things about mulberry. Researchers from South-Central University for Nationalities in China elaborated that mulberry fruit contains a great diversity of nutritive compounds as well as bioactive components, such as rutin, quercetin, anthocyanins, chlorogenic acid, and polysaccharides. They credited these compounds with the antioxidant, neuroprotective, anti-atherosclerosis, immunomodulatory, anti-tumor, cholesterol-lowering, and anti-diabetic activities shown by mulberry fruit extracts in in vivo and in vitro studies.
Because of the abundance of scientific evidence, all three articles concluded that mulberry fruit is a promising alternative treatment for chronic diseases like heart disease and diabetes.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
alternative medicine, anthocyanins, anti-atherosclerosis, anti-diabetes, anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, antioxidant, Chinese medicine, cholesterol-lowering, clean food, diabetes cure, diabetes mellitus, diabetes science, disease treatments, food cures, food is medicine, functional food, glucose absorption, heart disease, heart health, herbal medicine, herbal medicines, Herbs, inflammation, medicinal plants, metabolic disorder, metabolic health, Mulberry, natural cures, natural medicine, neuroprotective, phytonutrients, polyphenols, prevent diabetes, prevention, remedies, research, TCM
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author