Clinical trials reveal the effects of daily consumption of orange juice on blood lipids and gut flora
08/29/2019 / By Melissa Smith
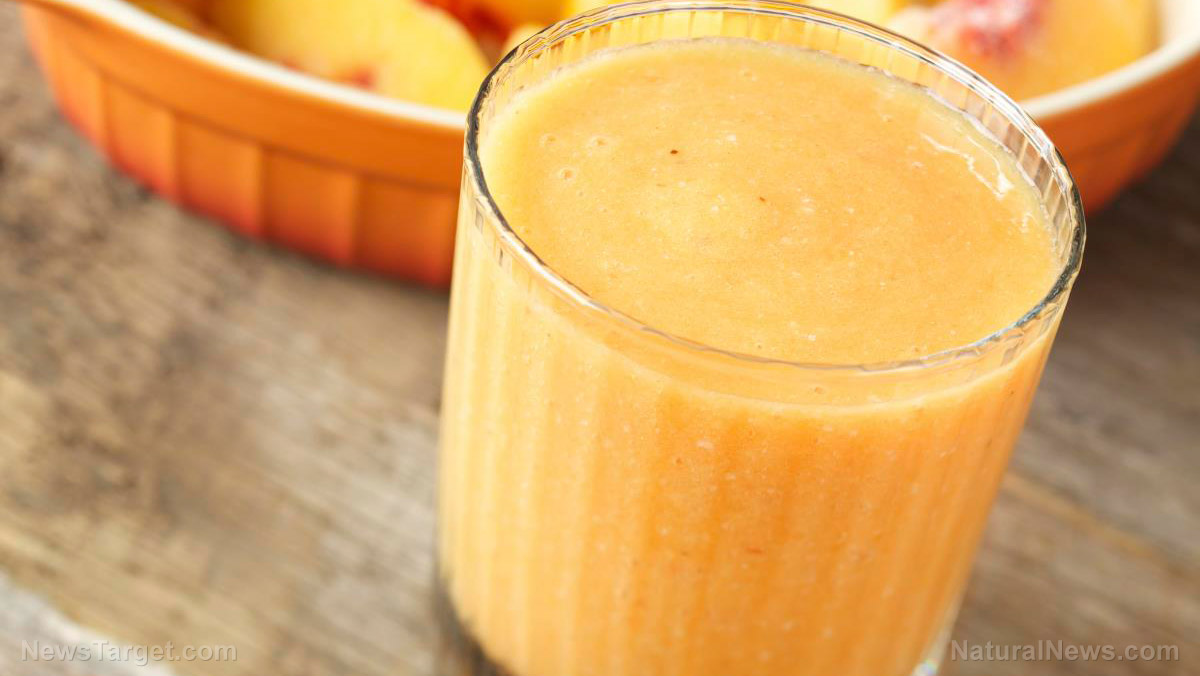

A team of researchers from Sao Paulo State University and the University of Sao Paulo in Brazil evaluated the effects of daily orange juice consumption on blood lipids, lipids, and gut flora. They published their findings in the Journal of Medicinal Food.
- Gut microbiota can be improved by consuming bioactive compounds like hesperidin and naringin, which can be found in citrus fruits like oranges and orange juice.
- The research team examined 10 healthy women who consumed orange juice every day for two months.
- Then, they collected samples of blood serum and stool for biochemical and microbiology assays.
- The researchers examined the participants’ intestinal microbiota for total anaerobic bacteria, Lactobacillus spp., Bifidobacterium spp., and Clostridium spp. They also conducted an independent culture evaluation.
- In addition, the pH, ammonium (NH4+), and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) were evaluated for microbial metabolism.
- The research team found that consuming orange juice daily did not change the participants’ body composition.
- However, it improved blood biochemical parameters, such as low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, glucose, and insulin sensitivity.
- Orange juice also positively modulated the composition and metabolic activity of gut microbiota, increasing the population of fecal Bifidobacterium spp. and Lactobacillus spp.
- They also found that microbial metabolism showed a reduction in ammonia levels and an increase in the production of SCFAs.
- These results suggested that consuming orange juice every day may improve the intestinal microbiota and metabolic biomarkers of young women.
The research team concluded that orange juice may be an effective health drink to improve gut health and metabolism.
Journal Reference:
Lima ACD, Cecatti C, Fidélix MP, Adorno MAT, Sakamoto IK, Cesar TB, Sivieri K. EFFECT OF DAILY CONSUMPTION OF ORANGE JUICE ON THE LEVELS OF BLOOD GLUCOSE, LIPIDS, AND GUT MICROBIOTA METABOLITES: CONTROLLED CLINICAL TRIALS. Journal of Medicinal Food. 23 March 2019; 22(2): 202-210. DOI: 10.3906/tar-1708-21
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
#nutrition, blood sugar, cardiovascular health, citrus fruits, diabetes, digestion, food cures, food is medicine, functional food, good bacteria, gut bacteria, gut health, heart health, Hesperidin, lipids, metabolism, naringin, Orange Juice, Oranges, phytonutrients, prevention, research, women's health
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author