Can black seed be used to lower blood pressure?
02/01/2019 / By Michelle Simmons
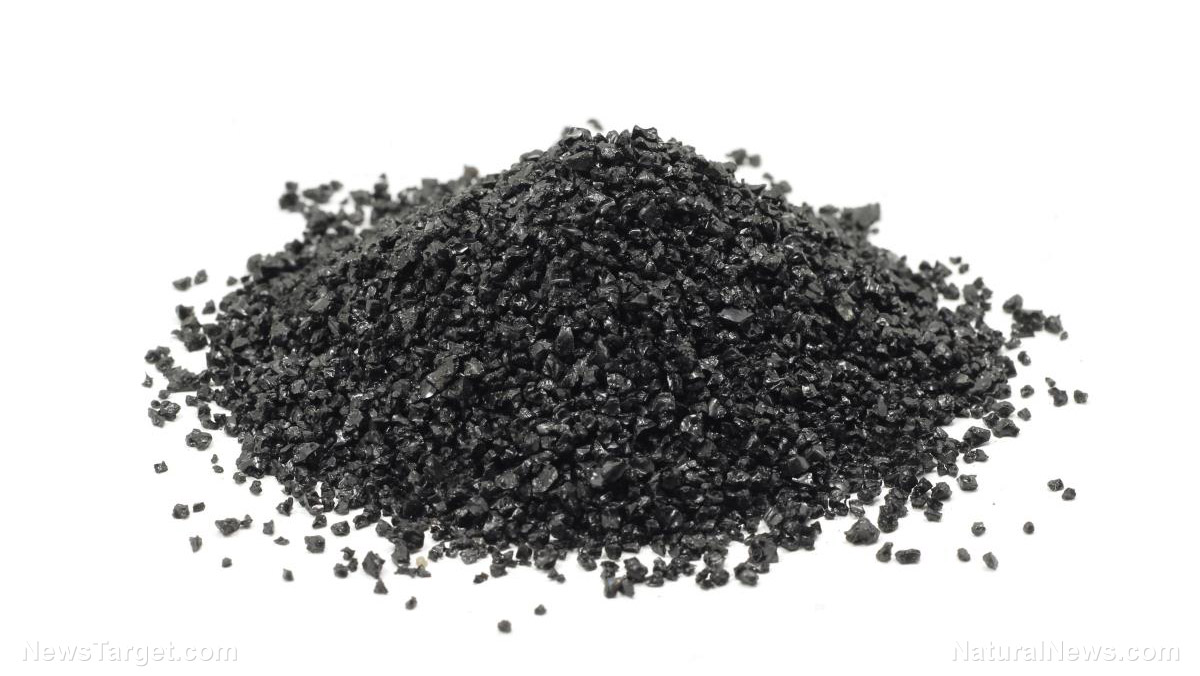

A research review published in the Journal of Hypertension confirmed that black seed (Nigella sativa) can significantly lower blood pressure. In the review, black seed significantly reduced both systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
- Various studies suggest that black seed has a beneficial effect on cardiometabolic risk factors, such as blood pressure. However, the magnitude of the blood pressure-lowering effect of black seed is not yet fully understood.
- Therefore, researchers aimed to measure this effect size of black seed through a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
- The researchers acquired 11 RCTs with a total of 860 healthy or hypertensive individuals.
- Ten of these RCTs compared black seed with placebo and one compared black seed with standard treatment.
- The researchers also looked at the associations between blood pressure reduction and the duration of treatment, dosage of black seed, and type of black seed.
- The data gathered showed that the average systolic blood pressure decreased from 132.85 to 125.19 millimeters of mercury (mmHg) after an average treatment duration of 8.3 weeks in black seed groups.
- The average diastolic blood pressure decreased from 82.63 to 77.74 mmHg after an average treatment duration of 8.3 weeks in black seed groups.
- There was a 59 percent difference in systolic blood pressure and a 60 percent difference in diastolic blood pressure between black seed and control groups.
- Black seed powder produced a more significant effect on both systolic and diastolic blood pressure compared to black seed oil.
- The researchers did not observe any association between systolic blood pressure lowering and time on treatment, black seed dosage or type of black seed.
Overall, these findings suggest that short-term treatment with black seed powder can substantially lower systolic and diastolic blood pressure levels.
To read more studies on natural treatments for high blood pressure, visit ReverseHeartDisease.news.
Journal Reference:
Sahebkar A, Soranna D, Liu X, Thomopoulos C, Simental-Mendia LE, Derosa G, Maffioli P, Parati G. A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS OF RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIALS INVESTIGATING THE EFFECTS OF SUPPLEMENTATION WITH NIGELLA SATIVA (BLACK SEED) ON BLOOD PRESSURE. Journal of Hypertension. November 2016; 34(11): 2127-2135. DOI: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001049
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
black cumin, black seed, blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, cardiovascular health, diastolic blood pressure, fennel seeds, Heart, heart disease, heart health, natural medicine, nigella sativa, systolic blood pressure
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author