Okra boosts your immune system
11/27/2018 / By Edsel Cook
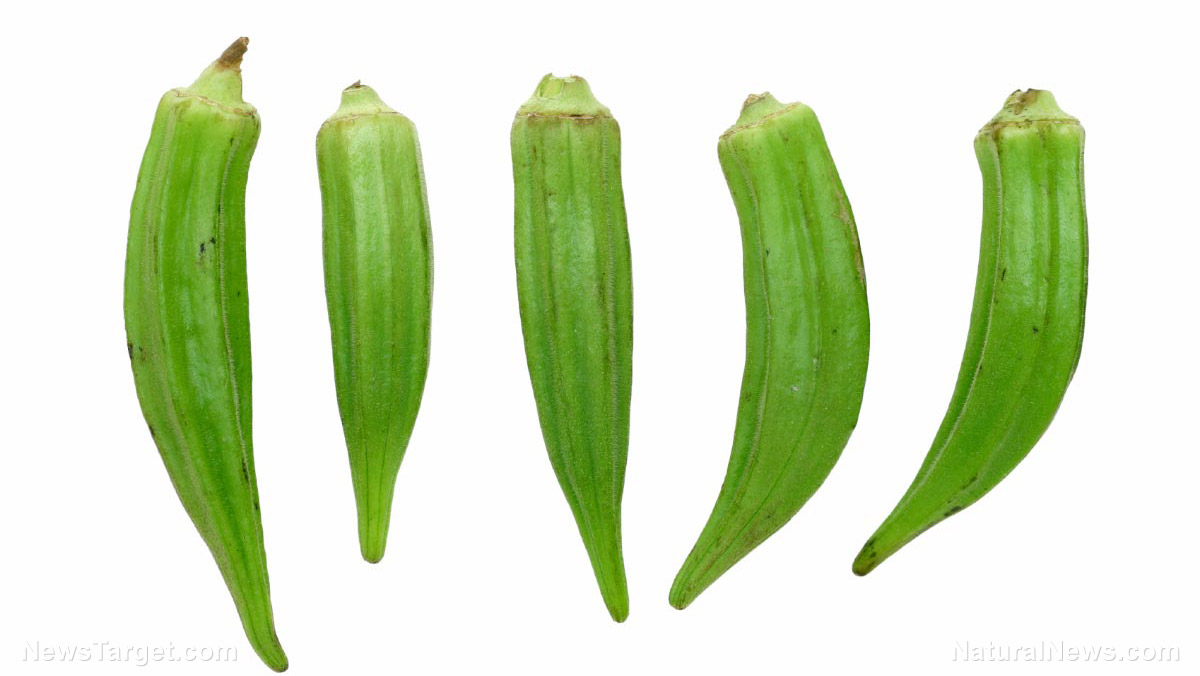

A Chinese study investigated the potential of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) as a means of supporting the immune system. They found that polysaccharides in the crude extract derived from the vegetable could strengthen the suppressed immune systems of mice.
The Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition provided support for the study. The findings were published in the Journal of Medicinal Food.
- Crude okra polysaccharide was extracted from the vegetable. The extract was further purified into three simpler fractions.
- The crude okra fractions were analyzed to determine the weight of their molecules, the monosaccharides that made up the polysaccharide, and their infrared and nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. Then they were administered to normal and immunosuppressed mice for evaluation of their ability to modulate the immune system.
- The molecules of the three purified fractions were 600, 990, and 1300 kilodaltons (kDa). The first two are mostly made up of galactose, galacturonic acid, glucuronic acid, and rhamnose, while the third fraction adds glucose to the mix. Spectra data of all three suggested their polysaccharide exhibited characteristics of rhamnogalacturonan I.
- The crude okra extract and its three fractions greatly increased many functions associated with the immune system. The production and release of cytokines like nitric oxide, inducible nitric oxide synthase, tumor necrosis factor alpha, interferon-gamma.
- In addition to immunomodulation, the second fraction (990 kDa) was also able to improve the spleen. It helped the production of splenocytes and the secretion of cytokines.
The researchers concluded that okra polysaccharides could be used as immune boosters for organisms with compromised immune systems.
Visit Veggie.news to read more articles about immune-boosting vegetables like the okra.
Journal Reference:
Chen H, Jiao H, Cheng Y, Xu K, Jia X, Shi Q, Guo S, Wang M, Du L, Wang F. IN VITRO AND IN VIVO IMMUNOMODULATORY ACTIVITY OF OKRA (ABELMOSCHUS ESCULENTUS L.) POLYSACCHARIDES. Journal of Medicinal Food. 2016;19(3):253–265. DOI: 10.1089/jmf.2015.3513.
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
benefits of okra, disease prevention, immune boosters, immune system, immunomodulators, immunotherapy, natural cures, natural medicine, Okra, polysaccharides, vegetables
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author