Here are foods that cause or prevent inflammation
09/13/2018 / By Ellaine Castillo

Inflammation is one of the ways through which your body fights off infections. However, there are some cases where instead of helping your body, inflammation becomes a problem. This condition is called chronic inflammation.
If not properly managed, chronic inflammation could progress to cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, artherosclerosis, and many other diseases. To reduce the symptoms of chronic inflammation, it is recommended that you follow an anti-inflammatory diet, such as the Mediterranean diet. The following video from Kwang Wellness discusses the different kinds of food that can trigger inflammation.
Watch the full episode from Brighteon.com here:
Foods that trigger inflammation
In the video, Kwang Wellness recommends avoiding foods that contain wheat and sugar, as they exhibit a synergistic effect that leads to more inflammation. By removing these foods from your diet, the symptoms of chronic inflammation will be reduced in just two weeks. (Related: The 5 Foods You May Want to be Avoiding in Your Diet.)
Studies show that excessive sugar intake can trigger an inflammatory response through different methods. First, excess sugars can increase the advanced glycation end products (AGE) made by your body. AGEs are formed when protein or fat molecules combine with sugar in the bloodstream. Excessive levels of AGEs in the bloodstream will lead to oxidative stress and inflammation.
Second, excess sugar in the body can increase gut permeability. This will allow bacteria, toxins, and food to move out of the gut and into the bloodstream. Once in the bloodstream, they will be detected as foreign materials, triggering an inflammatory response.
Mother Nature's micronutrient secret: Organic Broccoli Sprout Capsules now available, delivering 280mg of high-density nutrition, including the extraordinary "sulforaphane" and "glucosinolate" nutrients found only in cruciferous healing foods. Every lot laboratory tested. See availability here.
Third, sugar-rich diets can lead to excess body fats. Since there are more body fats present, there would also be a higher concentration of low-density lipoproteins (LDL) or “bad” cholesterol. An increase in LDL concentration is linked to more C-reactive proteins (CRP), which are biomarkers for inflammation.
It is also recommended to remove wheat from a person’s diet due to the amylase-trypsin inhibitors (ATI) that it contains. These ATIs trigger an inflammatory response that starts in the gut and can spread to other organs, including the brain, kidney, and spleen.
Aside from wheat and sugar, other foods that cause inflammation include:
- Dairy products – The intake of dairy can disrupt the cells of the guts, which will increase the permeability of these cells. This will allow foreign substances to move into the bloodstream and trigger an immune response.
- Processed meats – The consumption of meat, like sugar, is linked to an increase in CRP. Aside from this, meat intake is also linked to more arachidonic acid, a mediator that promotes inflammation.
- Fried foods – A study revealed that diets containing plenty of fried foods are linked to an increase in inflammation markers.
- Omega-6 fatty acids – Although it is necessary for growth and development, excessive intake of omega-6 fatty acids is bad for a person’s health. These fatty acids, which are found in soybean oil, vegetable oil, and mayonnaise, trigger the production of pro-inflammatory chemicals in the body.
Foods that should be included in an anti-inflammatory diet
Although some foods may exacerbate inflammation, there are others that are able to reduce inflammatory responses. These include:
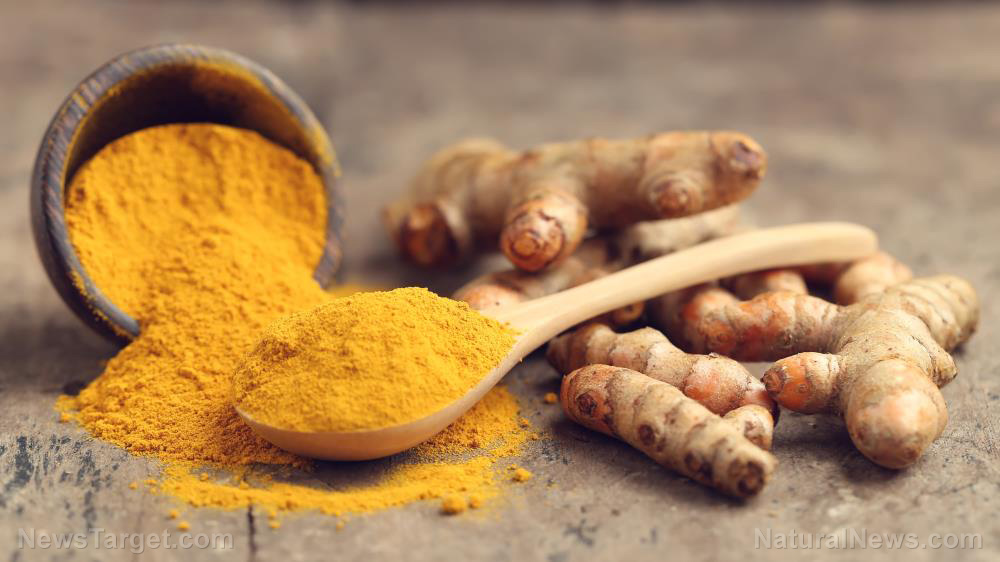
- Turmeric – researchers have observed that curcumin, a substance found in turmeric, possesses strong anti-inflammatory properties. Curcumin works by blocking NF-kb, which turns on the genes responsible for inflammation.
- Dark leafy greens – Kale, spinach, and collard greens are known for having natural antioxidants, which prevent inflammation by trapping free radicals that induce cell damage.
- Nuts – Studies show that people who eat nuts have reduced markers of inflammation.
- Apples – Similar to dark leafy greens, apples also contain natural antioxidants and polyphenols.
This video, which discusses foods that cause inflammation, can be viewed at this link.
Learn more about anti-inflammatory diets by visiting Nutrients.news today.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: anti-inflammatory diet, chronic inflammation, Diets, Diseases, functional food, grocery, inflammation, nutrients, nutrition, prevention, sugar, toxic ingredients, wheat, wheat protein