Study: Antibiotics are INEFFECTIVE for eczema
09/05/2018 / By Michelle Simmons
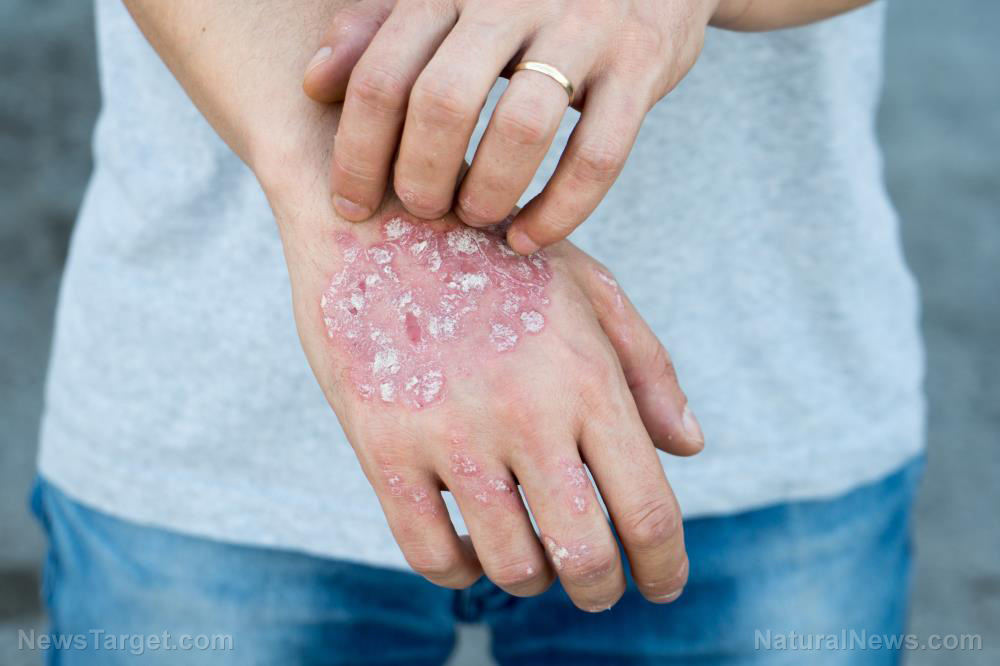
In addition to the side effects that come with antibiotic use, it turns out that most of them are ineffective. A study led by Cardiff University revealed that using either oral or topical antibiotics do not provide any beneficial effect for mild eczema in children. Furthermore, their use of antibiotics can even promote antibiotic resistance and allergy or skin sensitization. This is unfortunate because estimates suggest that 40 percent of eczema flares are treated with topical antibiotics.
The CREAM (ChildRen with Eczema, Antibiotic Management) study, which was published in the journal Annals of Family Medicine, aimed to determine if oral or topical (creams and antibiotics applied to the skin) antibiotics helped improve the severity of eczema in children. All children in the study also received standard eczema treatment with steroid creams and moisturizers from their doctor.
After analyzing data from a total of 113 children with mildly infected eczema, the research team discovered that there was no notable difference between the groups in the improvement of eczema symptoms at two weeks, four weeks, or three months.
The CREAM study was funded by the National Institute for Health Research Health Technology Assessment Programme.
Promising natural treatments for eczema
Eczema is the umbrella term for describing a group of medical skin conditions that cause red, inflamed, and itchy skin. In the U.S., there are about 31.6 million people that suffer from at least one type of eczema. Unfortunately, there is still no cure for eczema. Still, there are many safe and effective natural treatments for eczema that may help improve its symptoms. Here are some of the natural medicines that may help restore skin moisture and provide protection to skin’s natural barrier:

- Acupuncture and acupressure – The application of pressure using needles (acupuncture) or fingers and hands (acupressure) can help relieve eczema by improving itchy skin and other symptoms, according to research.
- Calendula cream – Calendula has been used as a folk remedy to relieve skin inflammation, burns, and cuts. It is also believed to enhance blood flow to areas of injury or inflammation, help moisturize skin, and help fight infection.
- Coconut oil – Coconut oil, which is extracted from coconut meat, may be used as a natural moisturizer. Research has shown that the antibacterial properties of coconut oil can decrease the number of staph bacteria on the skin, helping prevent infection. Just make sure that you’re using virgin coconut oil that is not processed without chemicals.
- Colloidal oatmeal – Colloidal oat is derived from finely-ground oats and is available in cream or powder form. This natural remedy can help calm and soften inflamed skin. To use, add the powder to lukewarm bathwater and soak for 10 to 15 minutes. After your bath pat your skin dry, then apply a thick layer of a hypoallergenic moisturizer that is high in oil. (Related: Top 15 Natural Home Remedies for Eczema.)
- Evening primrose oil – Evening primrose oil, which is derived from the evening primrose plant, is used topically to relieve irritated skin. It can also be taken orally to treat systemic inflammatory conditions like eczema. This oil also contains omega-6 fatty acids and gamma-linolenic acid, which may contribute to the prevention of inflammation in the body.
- Relaxation techniques – Eczema is commonly triggered by stress, which plays a role in developing inflammation. Learning to relieve stress using relaxation techniques may help decrease eczema flare-ups. Some relaxation techniques you can try include meditation, cognitive behavioral therapy, deep breathing, music therapy, and yoga.
- Sunflower oil – Extracted from sunflower seeds, sunflower oil can protect the outer layer of the skin, keeping the moisture and bacteria out. This oil also keeps the skin hydrated and may alleviate itching and inflammation.
- Witch hazel – Made from the bark and leaves of the witch hazel shrub, this astringent has been used for centuries as a topical remedy for skin inflammation.
Read more news stories and studies on antibiotic use by going to SuperBugs.news.
Sources include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
antibiotic resistance, antibiotic use, Antibiotics, children's health, eczema, eczema treatment, pediatric eczema, skin conditions
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author